
Reza Maroofian
@RMaroofian
Geneticist at UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology @UCLIoN. Interested in Rare Diseases, Neurogenetics & Genomic Medicine.
Our new study characterises ELFN1 deficiency as a novel autosomal recessive neurodevelopmental disorder marked by epilepsy, GDD/ID, & movement disorders. Biallelic ELFN1 variants disrupt synaptic protein trafficking—validated through functional assays and mouse/zebrafish models.
Neurogenetics alert! Biallelic loss of function variants in ELFN1 cause a neurodevelopmental disorder with DD/ID, seizures and movement disorder. bit.ly/4lLrZ46 @rhysdore
We define the recessive ELOVL1-related disorder, part of an emerging group of neurocutaneous syndromes caused by biallelic ELOVL1/4 variants. Monoallelic ELOVL1/4/5 variants lead to spastic paraplegia & ataxia. These genes encode enzymes that elongate very-long-chain fatty acids.
An important study by Wong et al. on neuro-ichthyosis linked to biallelic ELOVL1 variants. In this hypomyelinating leukodystrophy, commonly observed abnormal movements included spasticity, head tremor, and myoclonus. loom.ly/wwx-XQ4
🚨 We’re hiring a highly motivated Postdoc! Join us at @UCLIoN to study the neurobiology of PSMF1, a new gene linked to Parkinson’s & neurodegeneration. Expertise in: 🔬 hPSCs 🧪 Neuronal/organoid modelling 📅 Apply by 16/07 📩 [email protected] 🔗 shorturl.at/zVuPJ…
The dystonin gene encodes three major isoforms: DST-a, -b, and -e. Jacob et al. report that variants exclusively affecting DST-b cause an autosomal recessive congenital myopathy, while variants that also affect DST-a cause a lethal contracture syndrome. tinyurl.com/3p99pu9j
Join our team at @UCLIoN as a Senior Research Technician and Analyst for Next Generation Sequencing 🧬 Play a key role in advancing neurogenetics research through cutting-edge sequencing. Apply now: bit.ly/44h3XX8 @UKDRI @UCLBrainScience @LRS_UCL
We define the critical role of the LGI1–ADAM22/23 pathway in developmental & epileptic encephalopathy (DEE)—essential for regulating synaptic transmission and brain excitability. Previously linked ADAM22 to DEE, now we report biallelic LGI1 & ADAM23 variants causing lethal DEE.
Hirano et al. define a novel neurological disease spectrum involving the LGI1–ADAM22/23 pathway, identifying ultra-rare biallelic LGI1 variants in developmental and epileptic encephalopathy, and a biallelic ADAM23 variant in lethal neonatal epilepsy. tinyurl.com/4cpc48fy
Combinatorial transcriptional regulation establishes subtype-appropriate synaptic properties in auditory neurons dlvr.it/TLCP5L
Biallelic loss-of-function variants in ZNF142 are associated with a robust DNA methylation signature affecting a limited number of genomic loci nature.com/articles/s4143… #hvhebron #neuroped
Loss of XRCC1 disrupts cerebellar development in zebrafish due to toxic PARP1 accumulation. Strikingly, parp1 knockdown rescues the XRCC1 phenotype, supporting PARP1 inhibition as a potential therapy in recessive XRCC1-related neurodegenerative disorders. nature.com/articles/s4159…

Proud to present our work identifying a role for DIAPH1 and gamma-actin in regulating DSB repair and how defects in this pathway give rise to human disease. Big thanks to everyone involved, especially Beth Woodward, Sudipta Lahiri and Anoop Chauhan. nature.com/articles/s4146…
We previously reported a novel recessive paediatric neurodegenerative disorder linked to BORCS8. Our latest study identifies BORCS5 as a new NDD gene, showing a broader neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative spectrum with clear genotype–phenotype correlation. Read the preprint:
Pathogenic variants in BORCS5 Cause a Spectrum of Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders with Lysosomal Dysfunction medrxiv.org/cgi/content/sh… #medRxiv
📣New from @RDExeter & co! 📄Bi-allelic UGGT1 variants cause a congenital disorder of glycosylation cell.com/ajhg/fulltext/…
Our lab characterises the autosomal recessive TRMT1-related neurodevelopmental disorder through a large cohort, patient cells, and zebrafish—linking defective tRNA methylation to intellectual disability and expanding the emerging group of "tRNAopathies". cell.com/ajhg/fulltext/….

For #RareDiseaseDay2025, @IonSynapse is celebrating the invaluable contributions of our international collaborators, whose dedication is driving ground-breaking advancements in rare disease research across the globe. ucl.ac.uk/ion/news/2025/…
As part of 2 parallel studies, we delineated a new subtype of neurodevelopmental disorder linked to biallelic GTF3C3 variants. One study models the disorder using zebrafish, while the other utilizes fly. Check both papers below: academic.oup.com/braincomms/adv… & sciencedirect.com/science/articl….
NDUFA13, a mitochondrial complex I subunit, was linked to complex I deficiency in only 3 patients. We now report 10 more, expanding the phenotypic spectrum, consolidating its role, & comparing it with other complex I deficiency subtypes. Check our paper: academic.oup.com/braincomms/art…

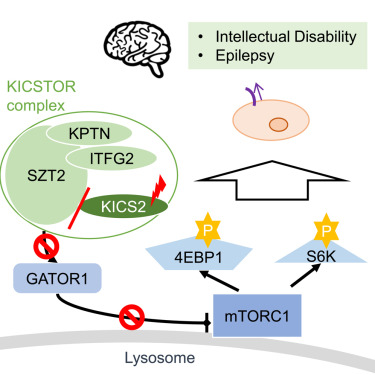
Back in 2013, we identified KPTN as a cause of NDD, though its function was unclear. By 2017, it was revealed as part of KICSTOR complex alongside KICS2, ITFG2, & SZT2, regulating mTORC1 signaling. We've now published KICS2 linked to NDD, with ITFG2 next. cell.com/ajhg/fulltext/…
TRMT1 & TRMT1L modify tRNAs, essential for protein production. Their modifications are crucial for tRNA stability & function. Biallelic TRMT1 variants are linked to intellectual disability, while TRMT1L variants lead to a recessive neurodegenerative disorder. Check our new paper!
TRMT1L-catalyzed m22G27 on tyrosine tRNA is required for efficient mRNA translation and cell survival under oxidative stress dlvr.it/THGZDC
In 2021, we identified a rare VWA1 founder mutation in UK & Western European populations, linked to neuromuscular disorder but elusive due to low genomic coverage. We now report an expanded phenotypic spectrum in a global cohort with this recurrent mutation & other VWA1 variants.
Nagy et al. report that VWA1-related motor neuropathy is linked to 11 novel mutations and diverse symptoms, including hypermobility and upper motor neuron signs. This highlights the diagnostic importance of understanding genetic and phenotypic variability. buff.ly/3ZZy57v