Mahesh
@gutsOfDarkness8
Engineering @AmadeusITGroup | Tech tips and tutorials to help you learn faster, grow stronger, and build great things. Now, let's talk through the content below
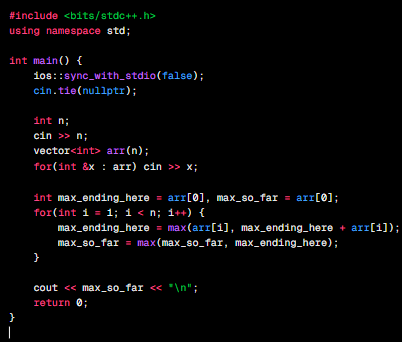
Maximum Subarray Sum: Kadane’s Algorithm efficiently finds the maximum sum of a contiguous subarray in an integer array. It runs in linear time, making it optimal for large input sizes, and is a classic example of dynamic programming used frequently in competitive programming.
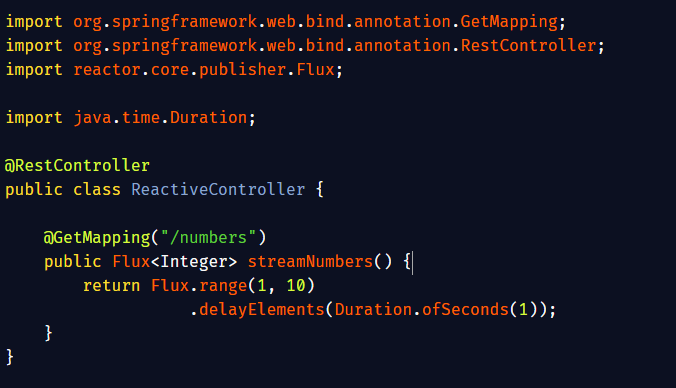
Building a Reactive REST API with Spring Boot and WebFlux: How to build a non-blocking, reactive REST API using Spring Boot with Spring WebFlux. Unlike traditional Spring MVC, WebFlux supports reactive programming with Project Reactor to handle asynchronous, event-driven data…

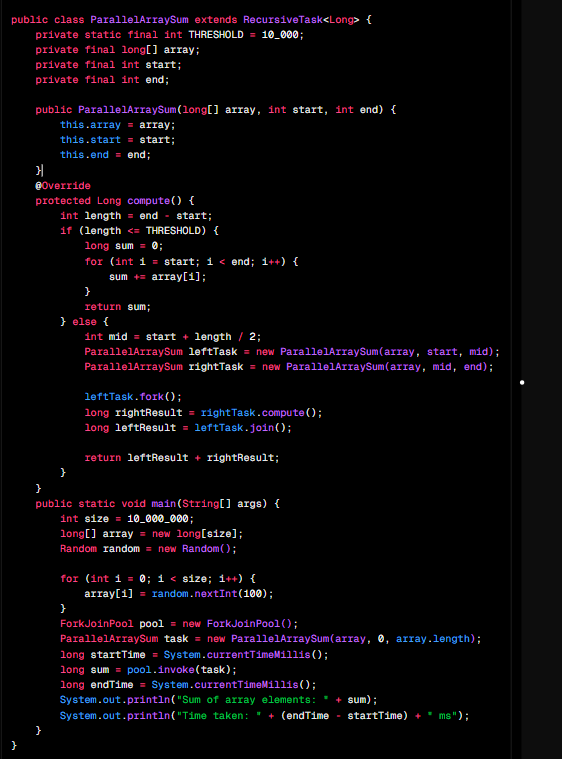
Parallel Sum of Large Arrays Using Java Fork/Join Framework: This program demonstrates how to use Java’s Fork/Join Framework (java.util.concurrent) to efficiently sum a large array by recursively splitting the task into smaller subtasks that can run in parallel. The RecursiveTask…
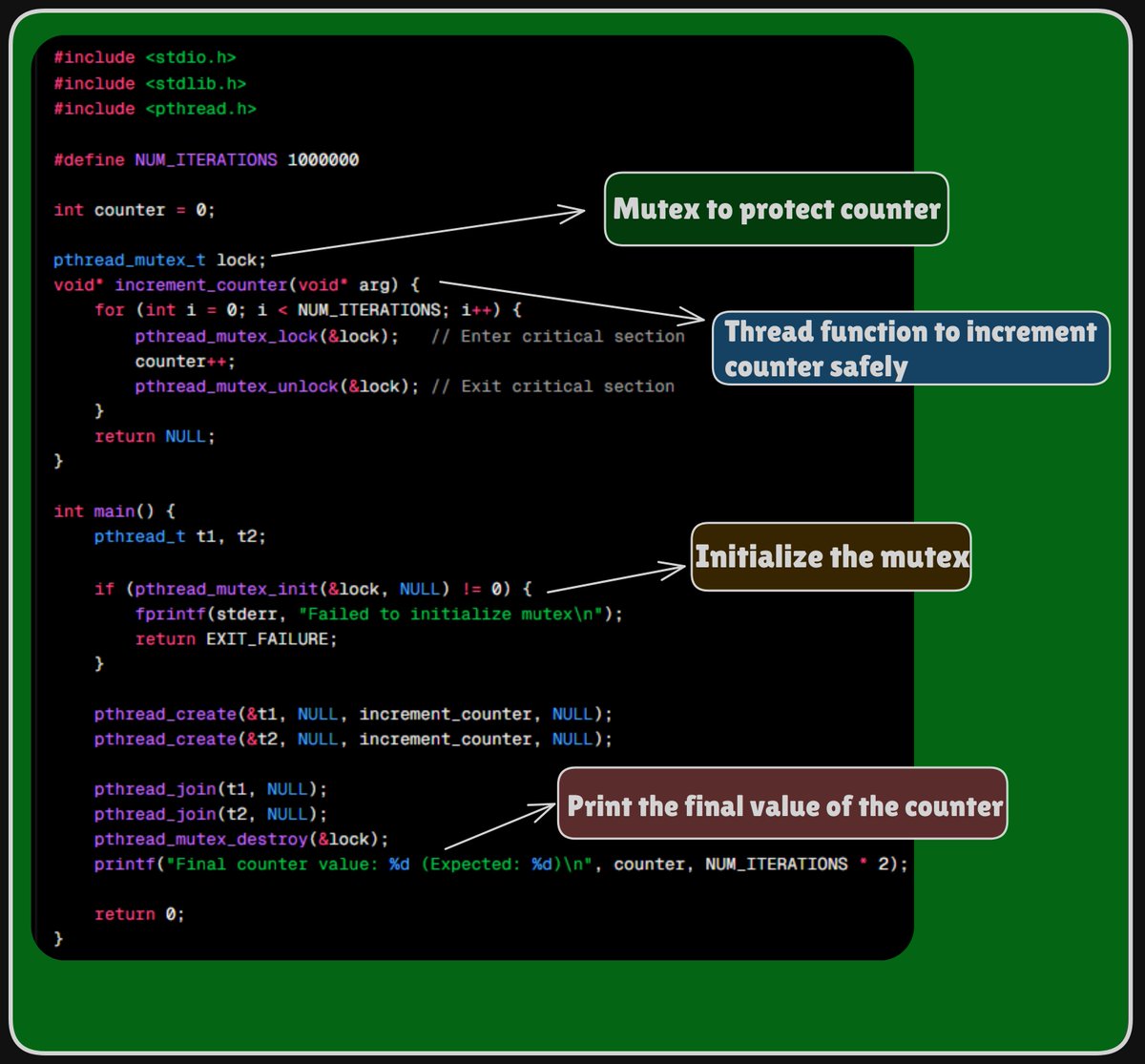
Thread-Safe Counter Increment Using POSIX Threads and Mutexes: This program demonstrates safe concurrent access to a shared resource in a multithreaded environment using POSIX threads (pthread). Two threads increment a shared global counter variable a million times each. To avoid…
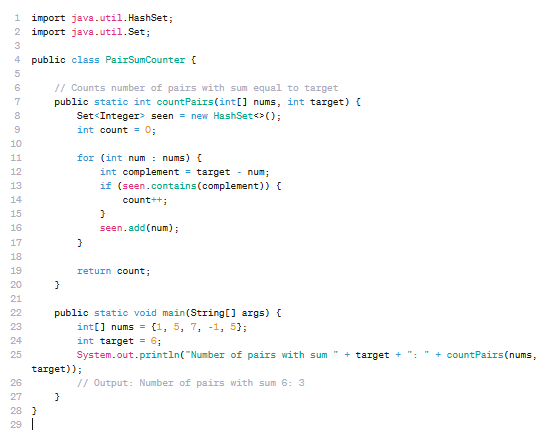
Efficient Problem Solving with Hashing: Is all about solving algorithmic problems efficiently and accurately under time constraints. One of the fundamental concepts is using hashing (via hash sets or maps) to optimize searches and count operations. This technique drastically…
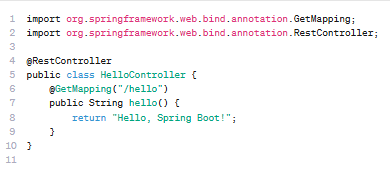
Simplifying Java Backend Development: Spring Boot is a powerful framework that streamlines Java backend development by removing the need for complex configuration. It provides embedded servers, auto-configuration, and starter dependencies so you can focus on building features…
Java Memory Allocation: Heap vs. Off-Heap (Direct ByteBuffer): In Java, memory is typically allocated on the heap using new. This is simple and garbage-collected, making it ideal for most applications. However, for high-performance or low-latency needs, Java offers off-heap…

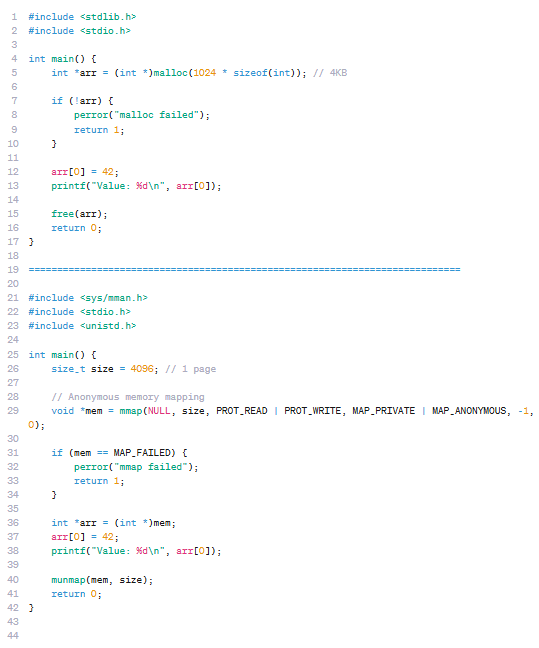
Traditional vs. Modern Memory Allocation malloc() vs. mmap(): In C, dynamic memory can be allocated using malloc(), a traditional method that uses the heap, ideal for general-purpose and small-sized allocations. It’s simple and widely used, with memory released using free().In…
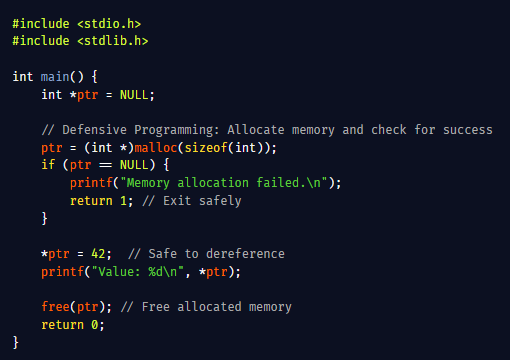
Longest Increasing Subsequence (LIS): Find the length of the longest strictly increasing subsequence in an integer array. This classic problem can be solved efficiently using binary search in O(n log n) time.
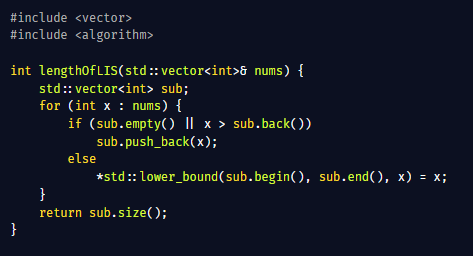
Spring Boot Profiles: Environment-Specific Configuration Made Easy Managing different configurations for development, testing, and production can become chaotic. Spring Boot simplifies this using Profiles, allowing you to isolate environment-specific settings cleanly. What Are…
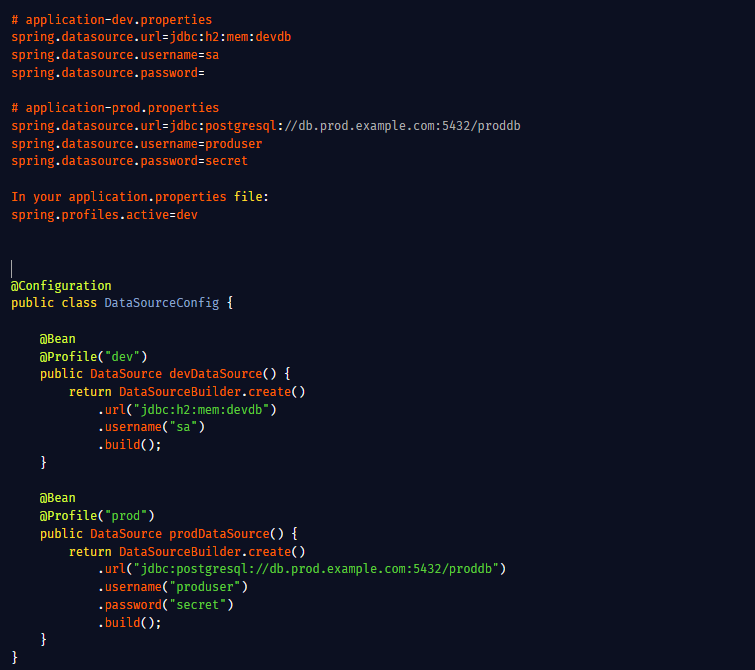
Memory Model & volatile Keyword: In multithreaded Java applications, ensuring visibility and consistency of shared variables is critical. This is where the Java Memory Model (JMM) and the volatile keyword come into play. What is the Java Memory Model (JMM)? The JMM defines how…
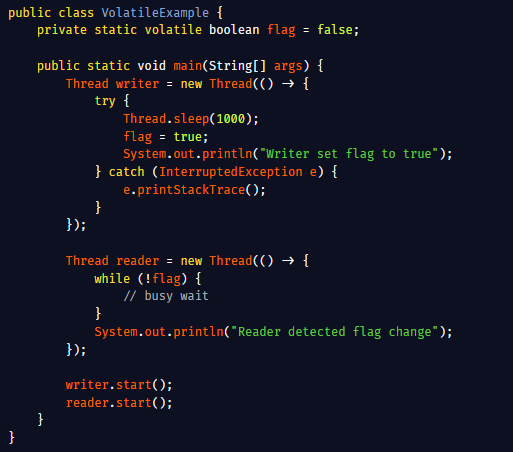
Undefined Behavior and Defensive Programming: Undefined Behavior (UB) refers to code operations for which the C standard does not prescribe any specific behavior. When a program encounters UB, it can produce unpredictable results crashes, incorrect outputs, or even seemingly…
Reactive Security with OAuth2 and JWT: Securing reactive applications is crucial in modern cloud-native environments. Spring Boot, combined with Spring Security, provides seamless integration for OAuth2 authorization and JWT (JSON Web Tokens) to secure your APIs in a…
Segment Trees for Fast Range Queries: Segment Trees are a versatile data structure that help you answer queries about intervals or ranges in logarithmic time. Whether you want to find the sum, minimum, maximum, or other associative operations over a range, segment trees make it…
Mastering Asynchronous Programming with CompletableFuture: CompletableFuture in Java provides a powerful way to write asynchronous, non-blocking code. It helps you handle multiple tasks concurrently, combine their results, and manage complex workflows without blocking threads.…
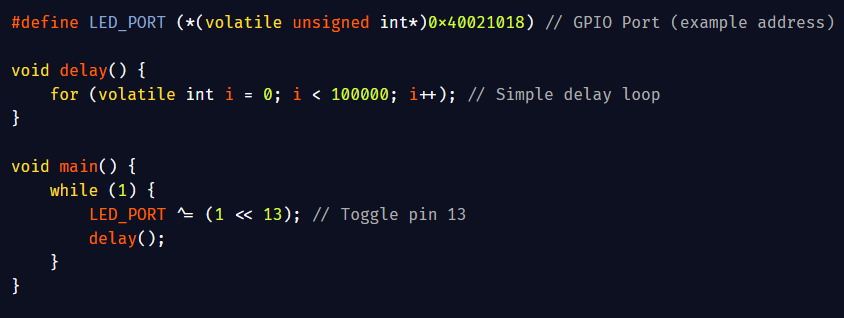
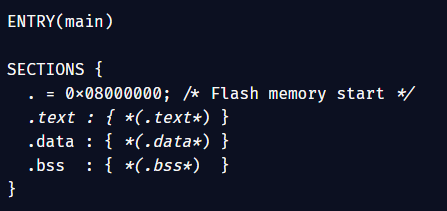
Memory-Mapped I/O (MMIO): Memory-Mapped I/O means that hardware devices (like sensors, timers, or LEDs) are controlled by reading and writing to special memory addresses. In C, we use pointers to access these addresses as if they were normal variables. Why use volatile? The…
Building Non-Blocking, Event-Driven Apps with Spring Boot WebFlux: Spring Boot’s WebFlux module lets you build non-blocking, event-driven applications that handle many requests efficiently without tying up threads. Instead of traditional synchronous calls, WebFlux uses Reactive…
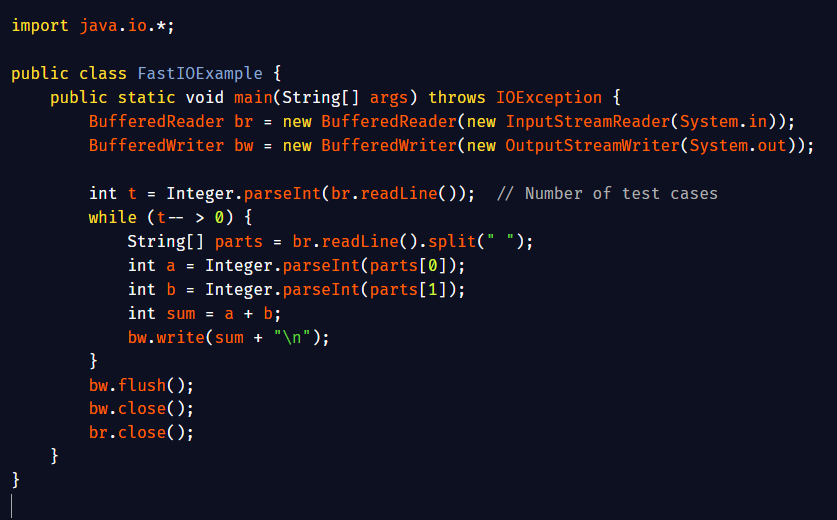
Fast Input/Output: In coding contests, reading and writing data fast is very important. Using BufferedReader and BufferedWriter instead of Scanner and System.out.println helps your Java program run much faster.
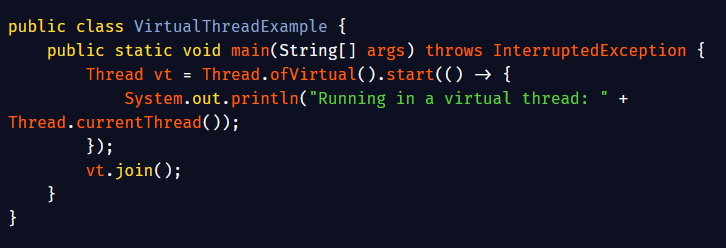
Virtual Threads with Project Loom: Traditional Java threads are powerful but heavyweight, limiting scalability in highly concurrent applications. Enter Project Loom introducing virtual threads, lightweight threads managed by the JVM that make concurrency simple and efficient.…
Bare-Metal No OS, No Runtime Just You and the Hardware: Step into the world of bare-metal programming, where there’s no operating system, no standard library, and no safety nets. You write code that talks directly to hardware using C perfect for real-time systems,…