Cell Host & Microbe
@cellhostmicrobe
The scientific editors of Cell Host & Microbe, a Cell Press journal, bring you the latest information and insights from the forefront of host-microbe research.
Our July issue is out today! Cover art depicts precision antibacterial strategies that allow non-toxigenic V. cholerae to dominate toxigenic rivals. cell.com/cell-host-micr…

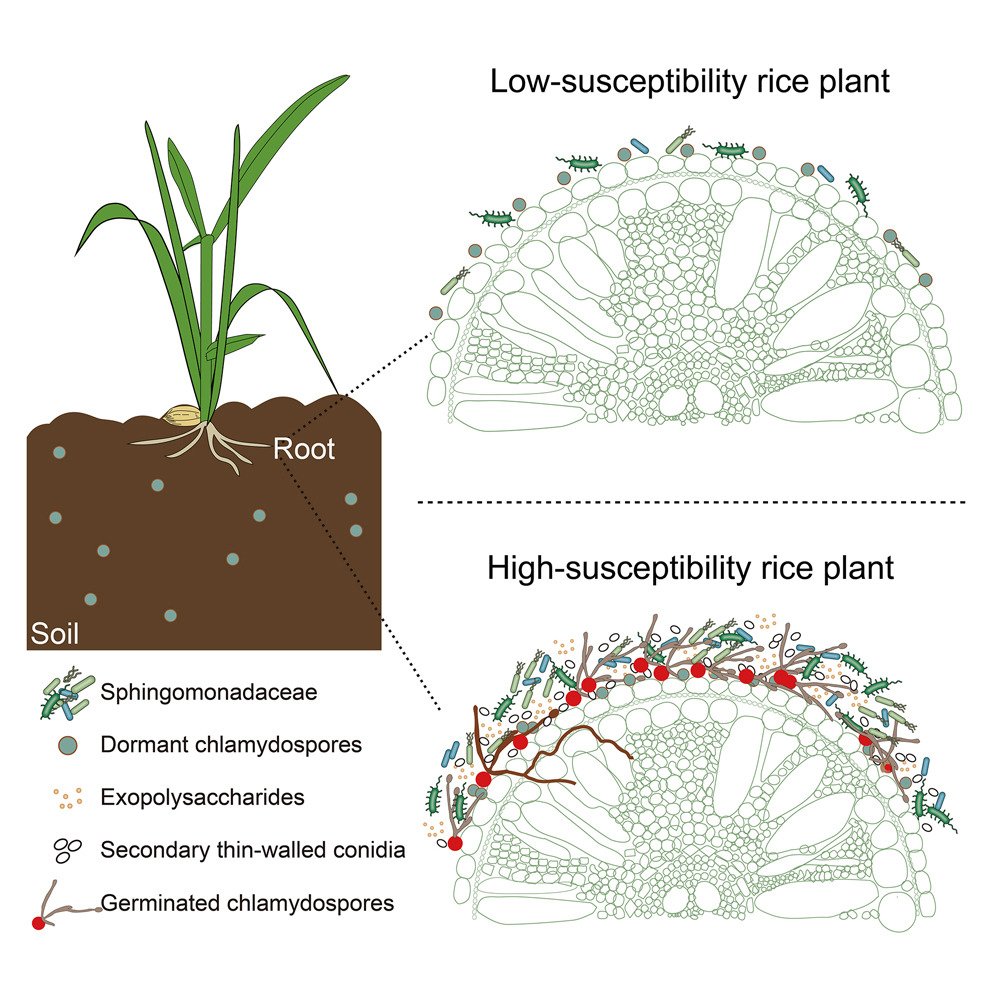
Collection: Plants!!! Browse our collection of recent reviews and articles on how microbes influence plant health, acting positively through beneficial interactions or negatively by causing disease. cell.com/cell-host-micr…
Collection: Bugs as Drugs. Enjoy our collection of recent reviews and articles exploring the impact of microbes on therapeutic efficacy as well as advancing capabilities to utilize microbes as therapeutics or in microbiome modulation cell.com/cell-host-micr…
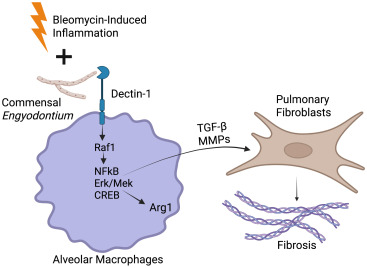
Fungal cues, fibrotic consequences: Highlight of @ImmunityCP work uncovering role for commensal fungi in lung fibrosis, showing that their interaction w/alveolar macrophages triggers profibrotic transcriptional program through Dectin-1-Raf1 signaling axis cell.com/cell-host-micr…
How hosts accurately command bacteria for gut health: Highlight of @Nature work revealing how hosts distinguish & respond to specific symbionts. Host APOL proteins engage Bacteroidales to trigger OMV release, which sustains gut immune homeostasis cell.com/cell-host-micr…
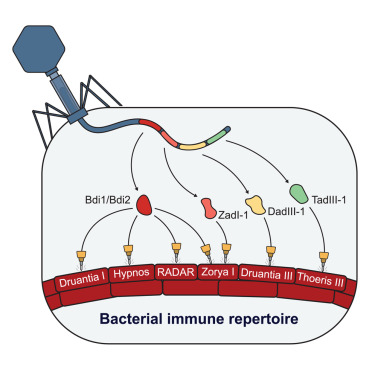
Phage counter-defense repertoires: New work IDs broad & specific anti-defense genes in variable regions of Pseudomonas phage genomes. Inhibitors neutralize diverse bacterial immune systems, highlighting how phages evolve broad & specific strategies cell.com/cell-host-micr…
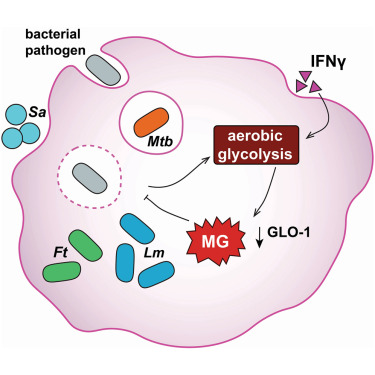
Waste as an antibacterial weapon: Elgrail & Glickman highlight work showing methylglyoxal, a metabolic byproduct of glycolysis, is part of macrophage arsenal limiting L. monocytogenes & MTb but is countered by pathogen methylglyoxal detoxification enzymes cell.com/cell-host-micr…

Methylglyoxal: antibacterial effector Methylglyoxal produced by infected macrophages upon transition to aerobic glycolysis acts as an innate immune antimicrobial effector that bacteria must detoxify for virulence and to prevent mutations cell.com/cell-host-micr…
Innate defense at onset of development: Embryos eliminate bacteria via phagocytosis by epithelial cells. Zebrafish embryos engulf bacteria via zippering protrusions, inducing program crucial for development. Phagocytosis conserved in mouse & human embryos cell.com/cell-host-micr…

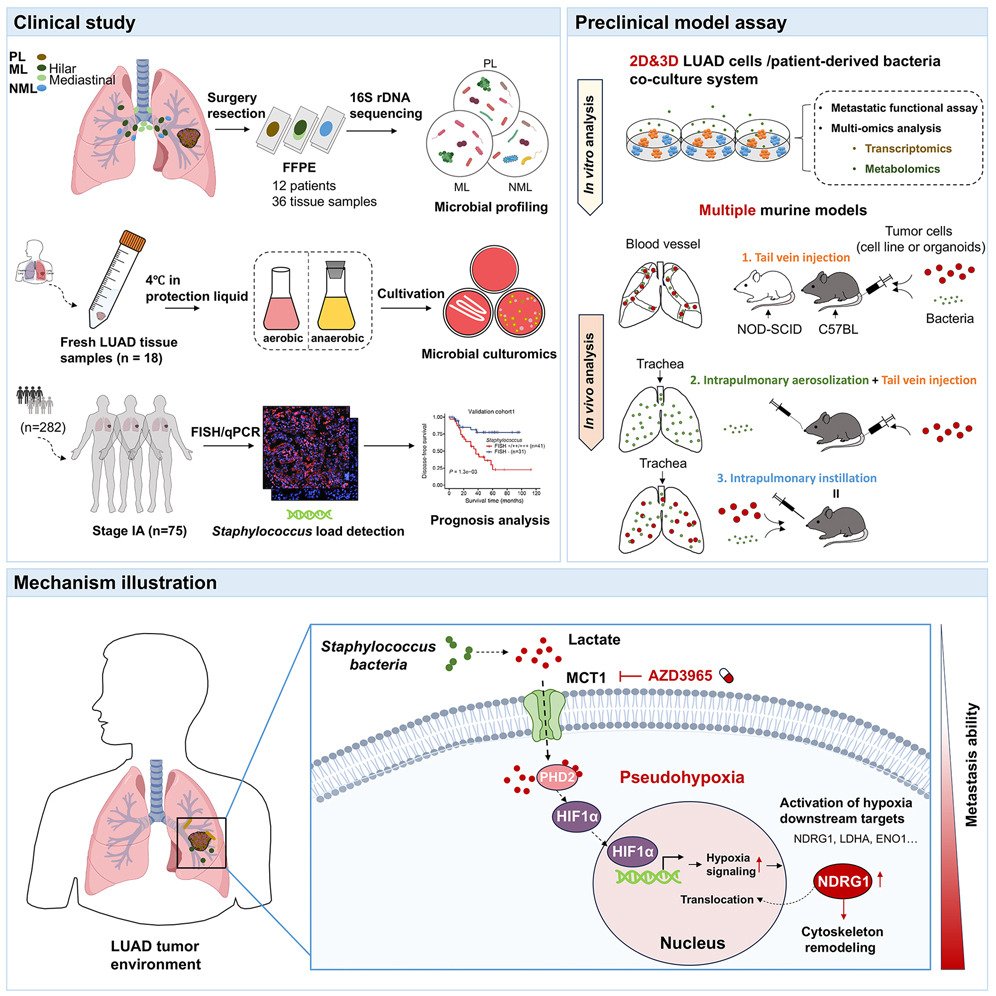
Staphylococcus promotes metastasis: · Staphylococcus enriched in metastatic lung tumor lesions · S. nepalensis & S. capitisl-secreted lactate promotes metastatic potential via MCT1-mediated pseudohypoxia signaling · MCT1 inhibition abolishes metastasis cell.com/cell-host-micr…
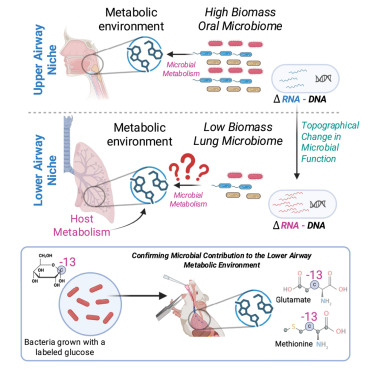
Upper vs lower airways: Microbes shape the local milieu Highlight of work on microbiome contribution to metabolism in upper vs lower airways. Oral commensals contribute to metabolic milieu w/P. melaninogenica synthesizing inosine&glutamate in lower airways cell.com/cell-host-micr…
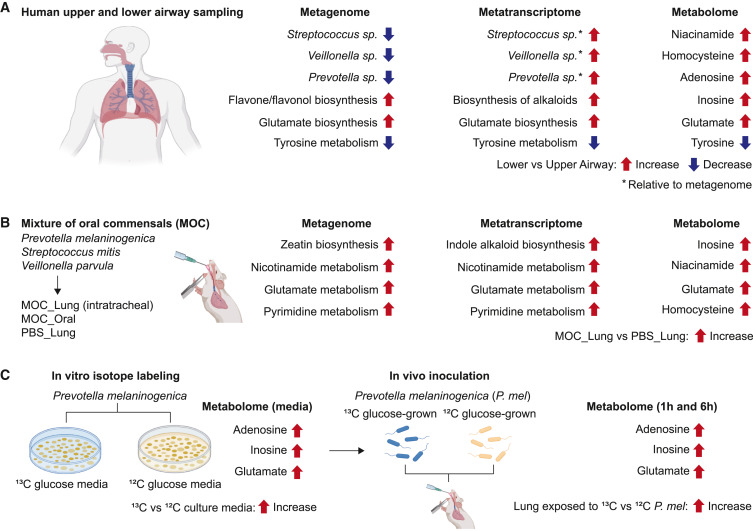
Lung microbes define metabolic niche: Microbial activity varies along respiratory tract, influencing metabolites & contributing to niche construction in lower airways. Lung microbiome directly influences metabolic pathways w/immunomodulatory effects. cell.com/cell-host-micr…
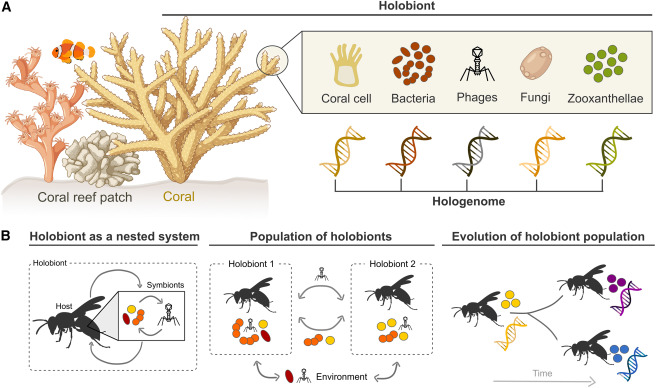
Theory of host-microbe symbioses: Challenges & opportunities Discussion on mathematical modeling of microbial symbioses w/ 3 areas requiring advancement: nested ecology w/in host or holobiont, holobiont population dynamics & symbiont-mediated speciation cell.com/cell-host-micr…
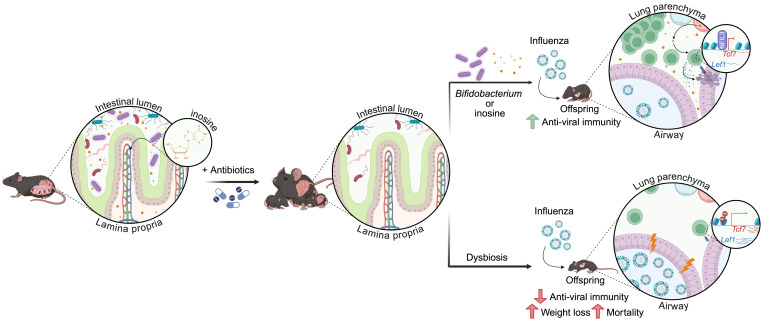
Bugged before birth? How maternal microbes reprogram offspring immunity Preview of @CellCellPress paper showing maternal antibiotic treatment induces dysbiosis & impairs offspring immunity to influenza. CD8 Tcell dysfunction reversed w/Bifido metabolite cell.com/cell-host-micr…
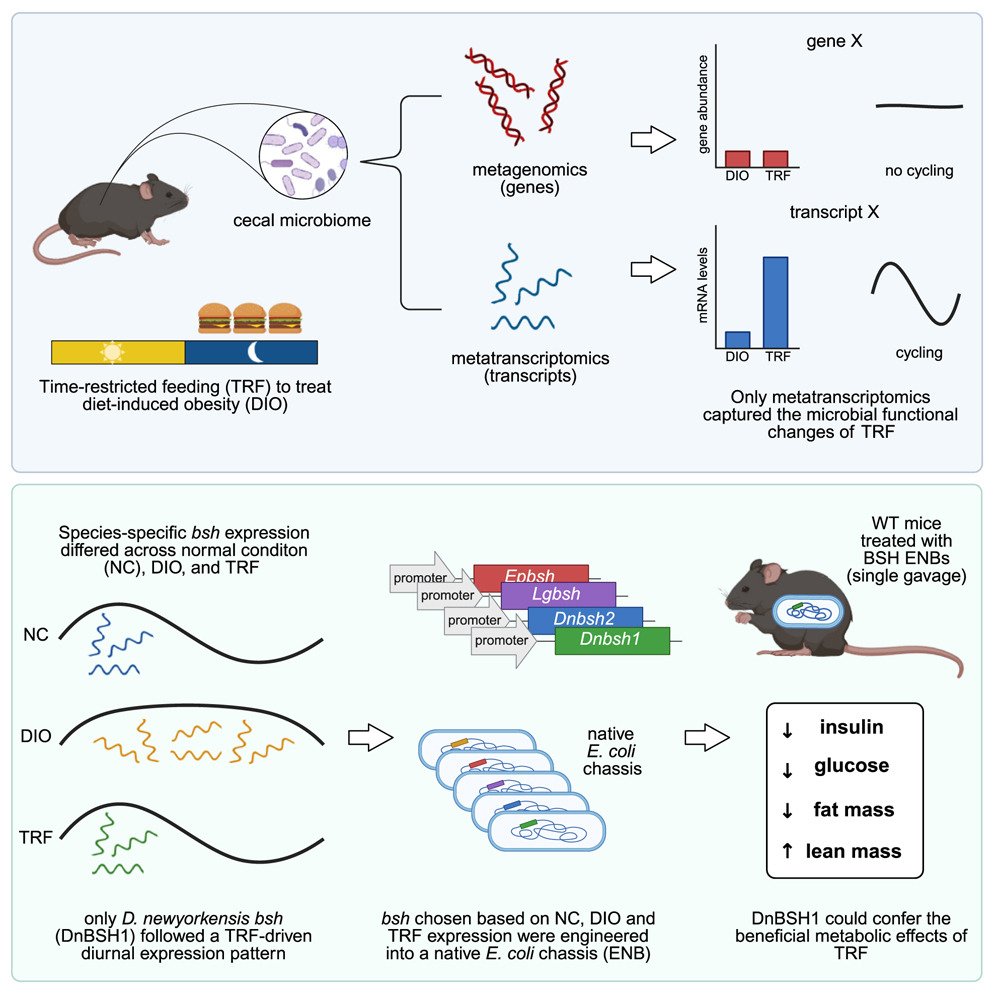
Metatranscriptomics catches gut microbes in the act: Preview of work employing metatranscriptomics to uncover diurnal microbial functional shifts in gut microbiome driven by time-restricted feeding, cell.com/cell-host-micr…

Featured Article: Leveraging diurnal shifts in bacterial transgenes: Time-restricted feeding causes diurnal functional shifts in microbes. D. newyorkensis BSH1 exhibits diurnal expression. DnBSH1-E. coli improves glucose metabolism&reduces body fat in mice cell.com/cell-host-micr…
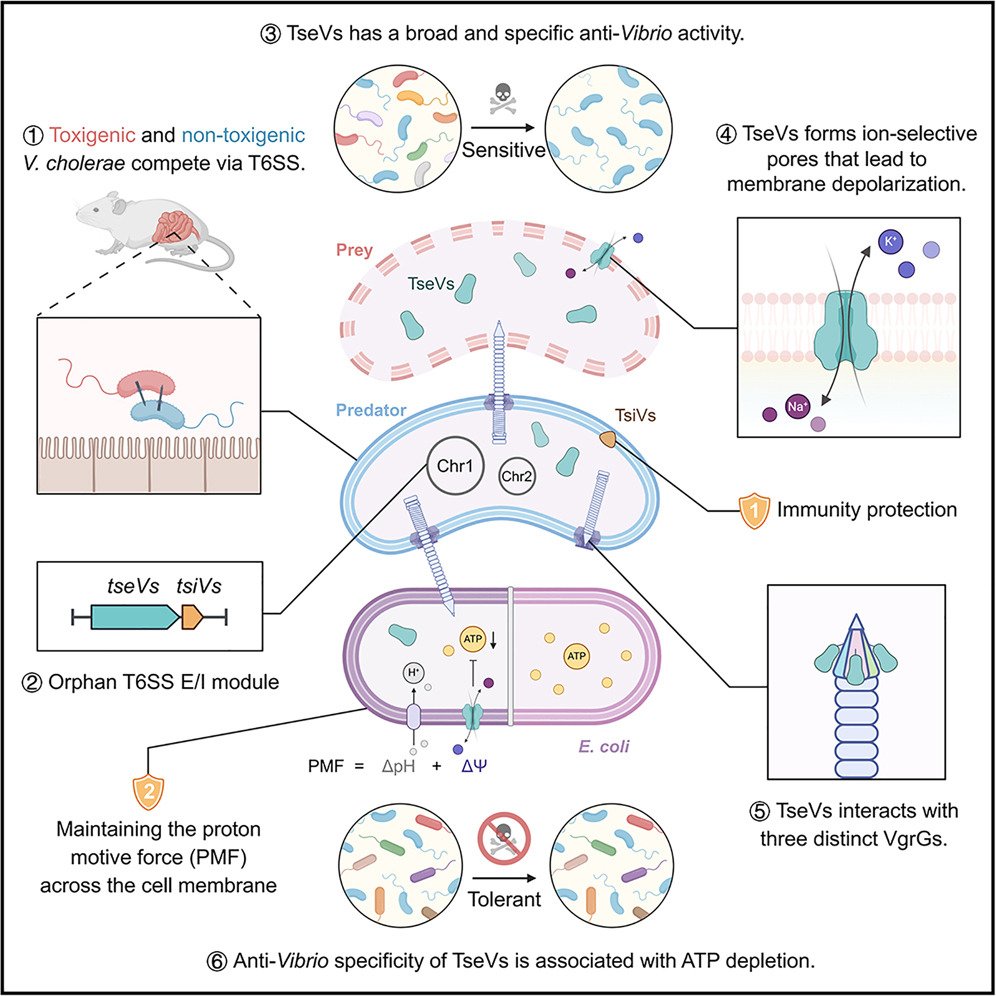
Featured Article: Vibrio T6SS effector joins the competition: Vibrio-specific T6SS effector, TseVs, selectively disrupts Vibrio bioenergetics while sparing non-target microbes via an immunity-independent mechanism. cell.com/cell-host-micr…
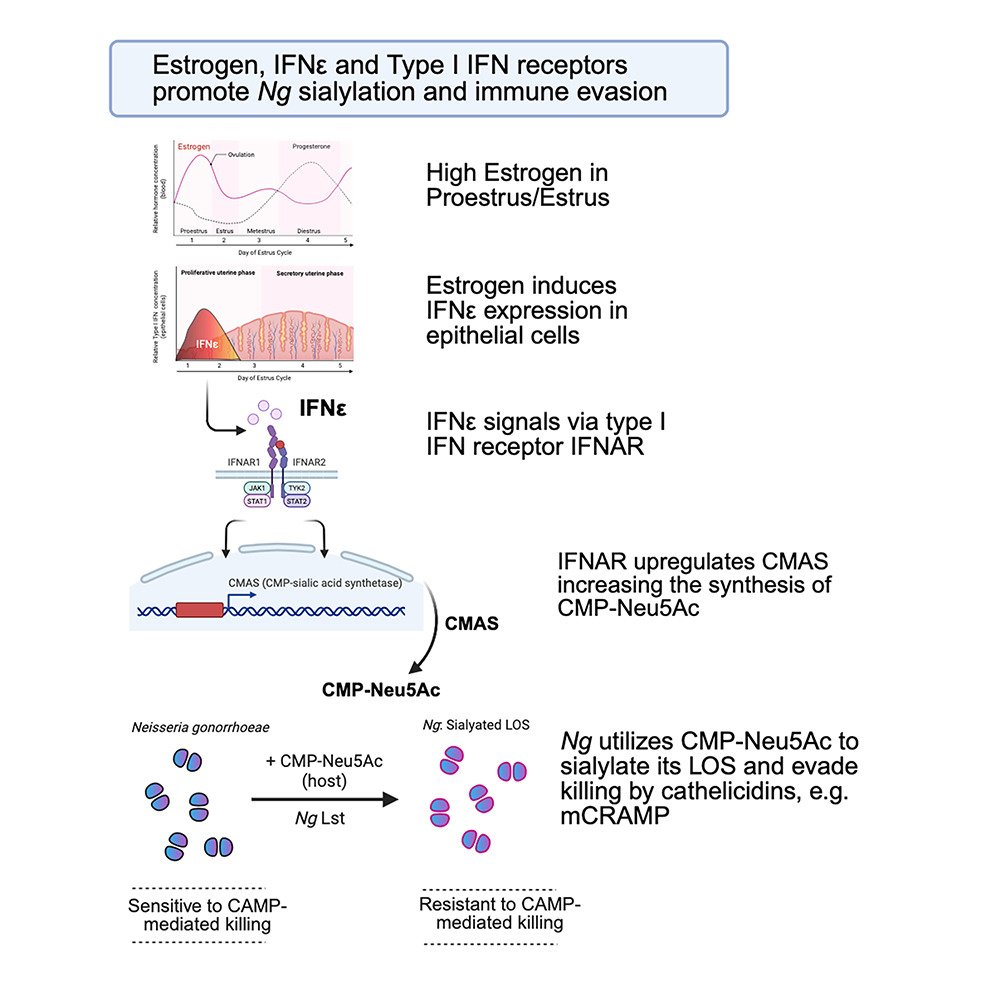
Type I IFNs give gonococci a sweet treat & a chance at survival. Dillard Previews work showing IFN-ε increases CMP-sialic acid production in epithelial cells, potentiating sialic acid modification of N. gonorrhoeae lipooligosaccharide for immune evasion cell.com/cell-host-micr…

Featured Article: IFN-ε shields Neisseria IFN-ε, a hormone-responsive type I IFN expressed by genital epithelial cells, boosts sialylation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which allows Neisseria to evade immune elimination cell.com/cell-host-micr…
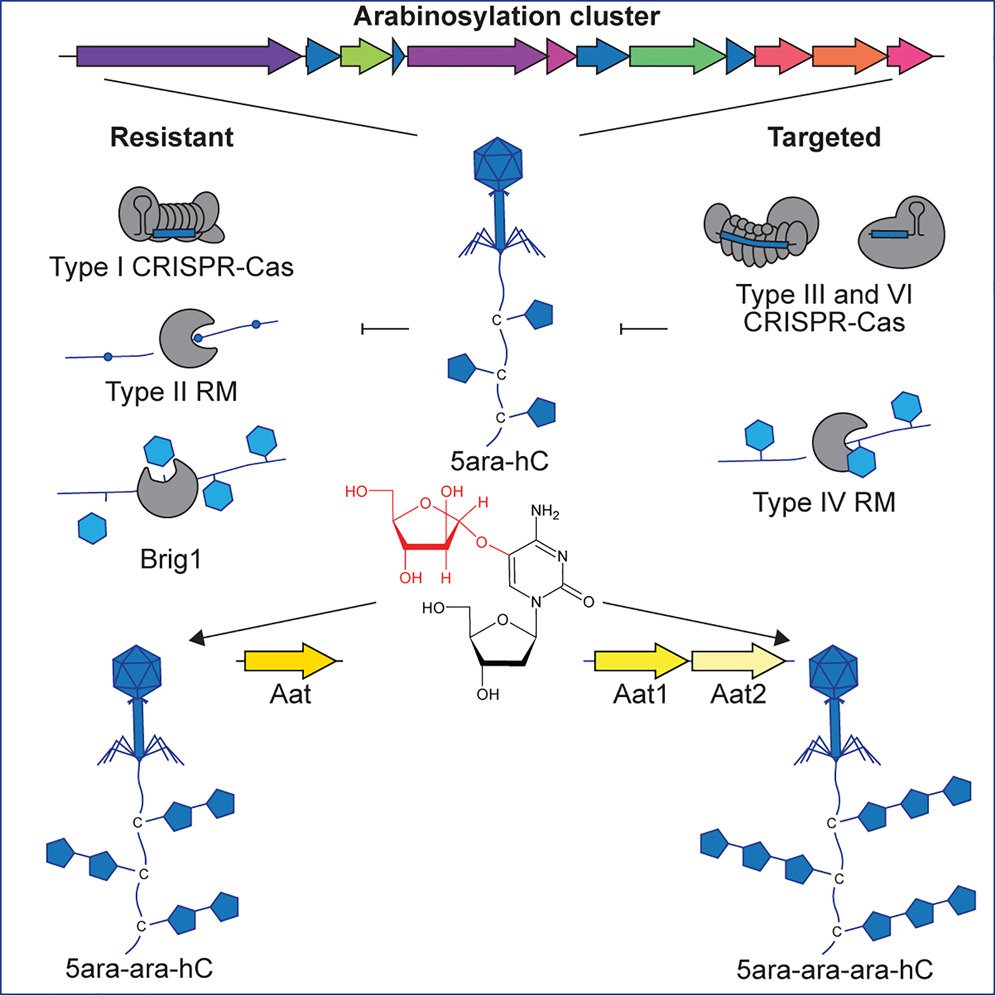
Featured Article: Phage DNA modifications evade defense Phage DNA modification adds arabinose to cytosines via hydroxy linkage(5ara-hC) w/potential double/triple arabinosylation. Arabinosylated phages are protected from CRISPR-Cas &restriction modification cell.com/cell-host-micr…