The Math Flow
@TheMathFlow
mathematics as an art form.
"The only way to learn mathematics is to do mathematics."

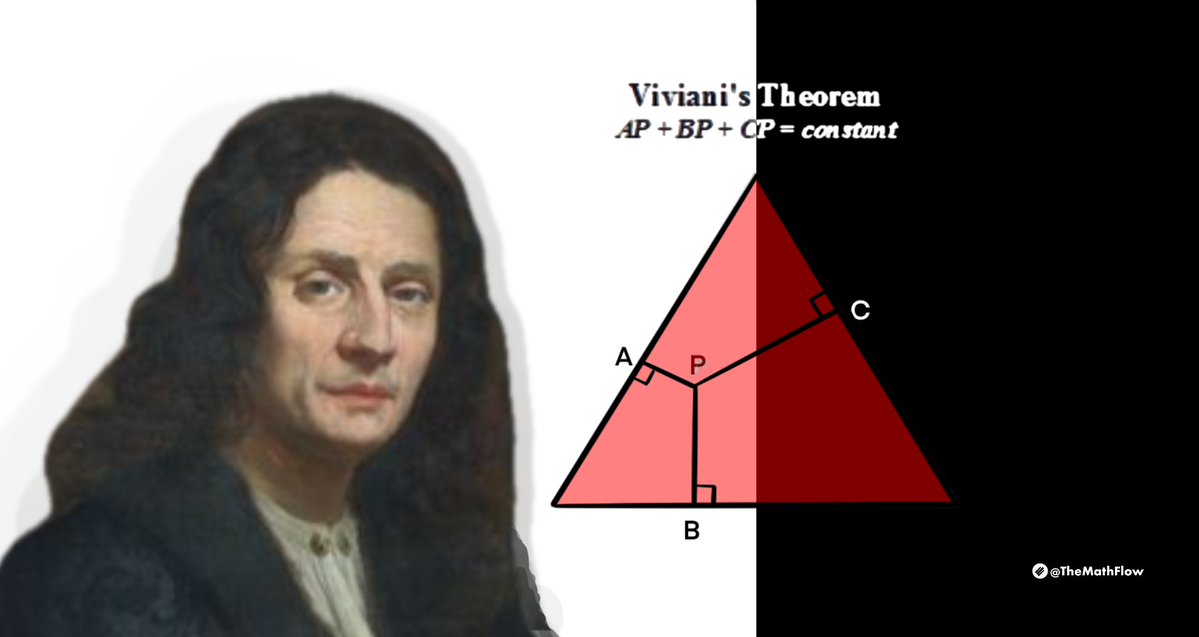
Viviani's theorem states that for any interior point within an equilateral triangle, the sum of the distances from that point to the three sides of the triangle is constant and equal to the length of the triangle's altitude.
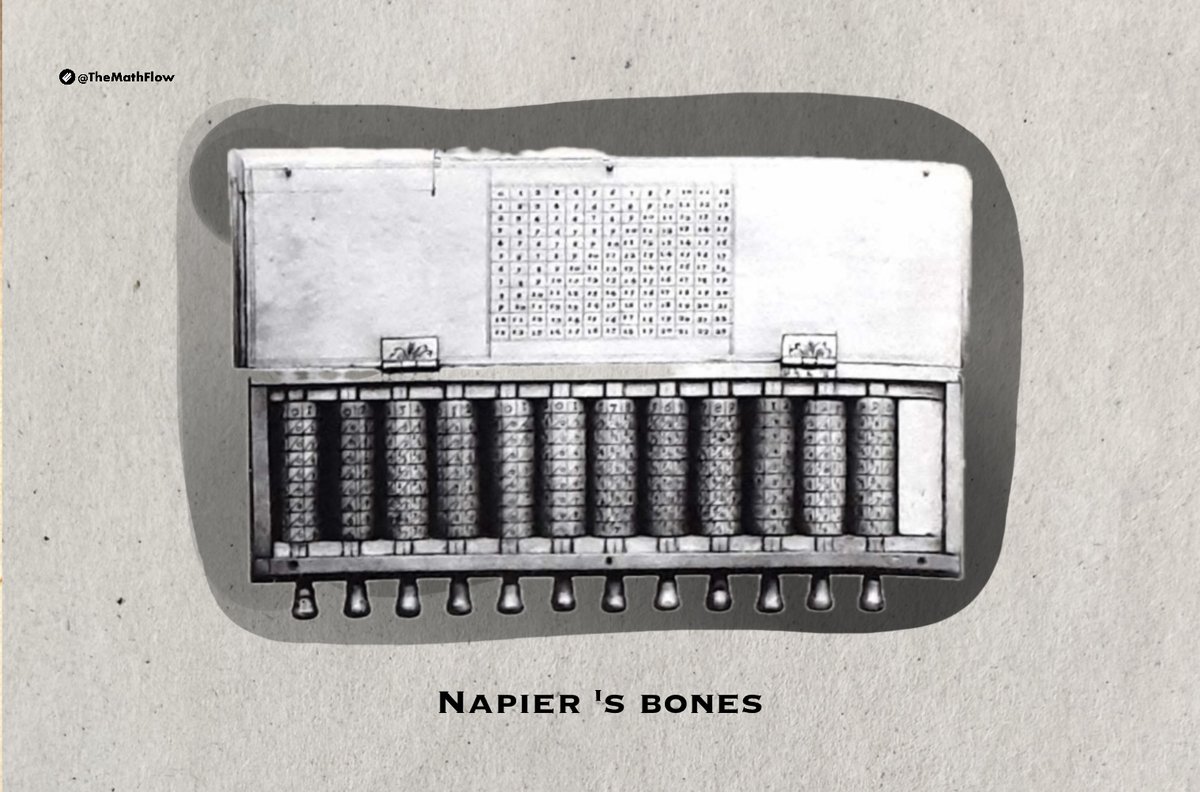
Napier's bones, also known as Napier's rods or rabdology, are a manually operated calculating device invented by Scottish mathematician John Napier in 1617 for simplifying the calculation of products (multiplication) and quotients (division) of numbers.
The use of letters to represent known constants and unknown quantities in equations was introduced by the 16th-century French mathematician François Viète. He used consonants for known quantities and vowels for unknowns.
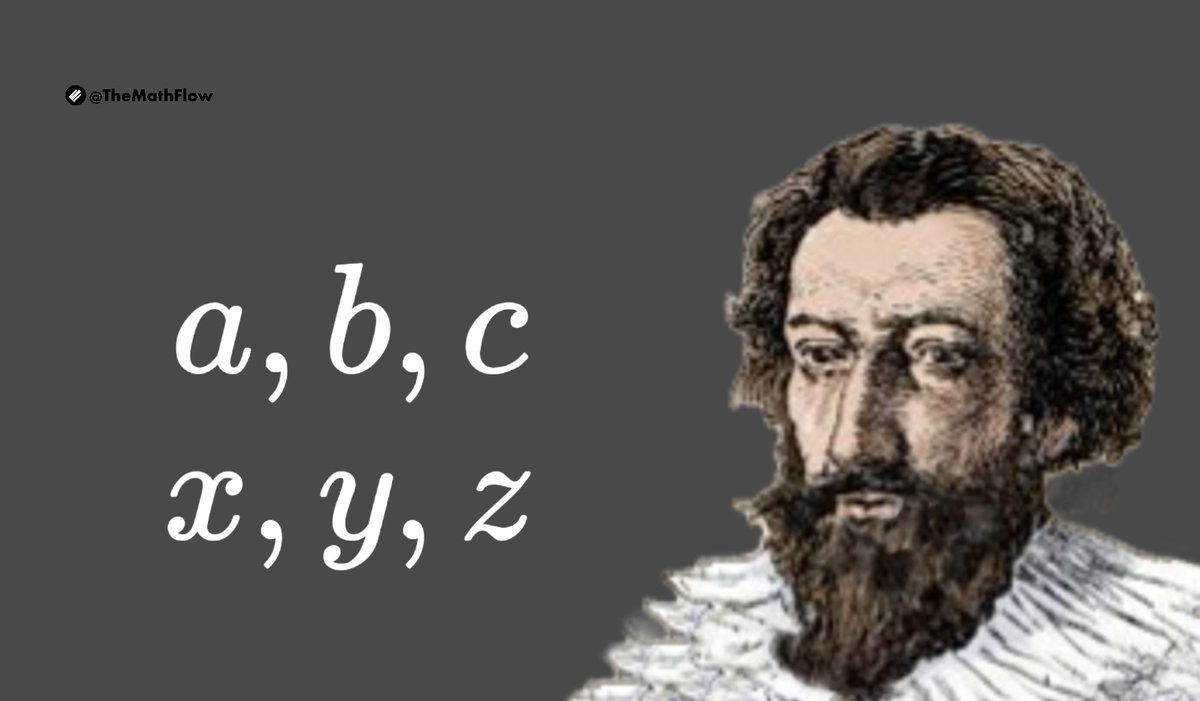
The first equals sign (=) appeared in the Whetstone of Witte, a 1559 math book by Englishman Robert Recorde.

The title page of Napier's Mirifici Logarithmorum Canonis Descriptio (Description of the Marvellous Canon of Logarithms), published in 1614.

John Napier, the inventor of logarithms, was an early proponent of using a dot to separate the integer part of a decimal number from its fractional part, contributing to the development of modern decimal notation. The idea of decimal calculations had been suggested earlier by the…

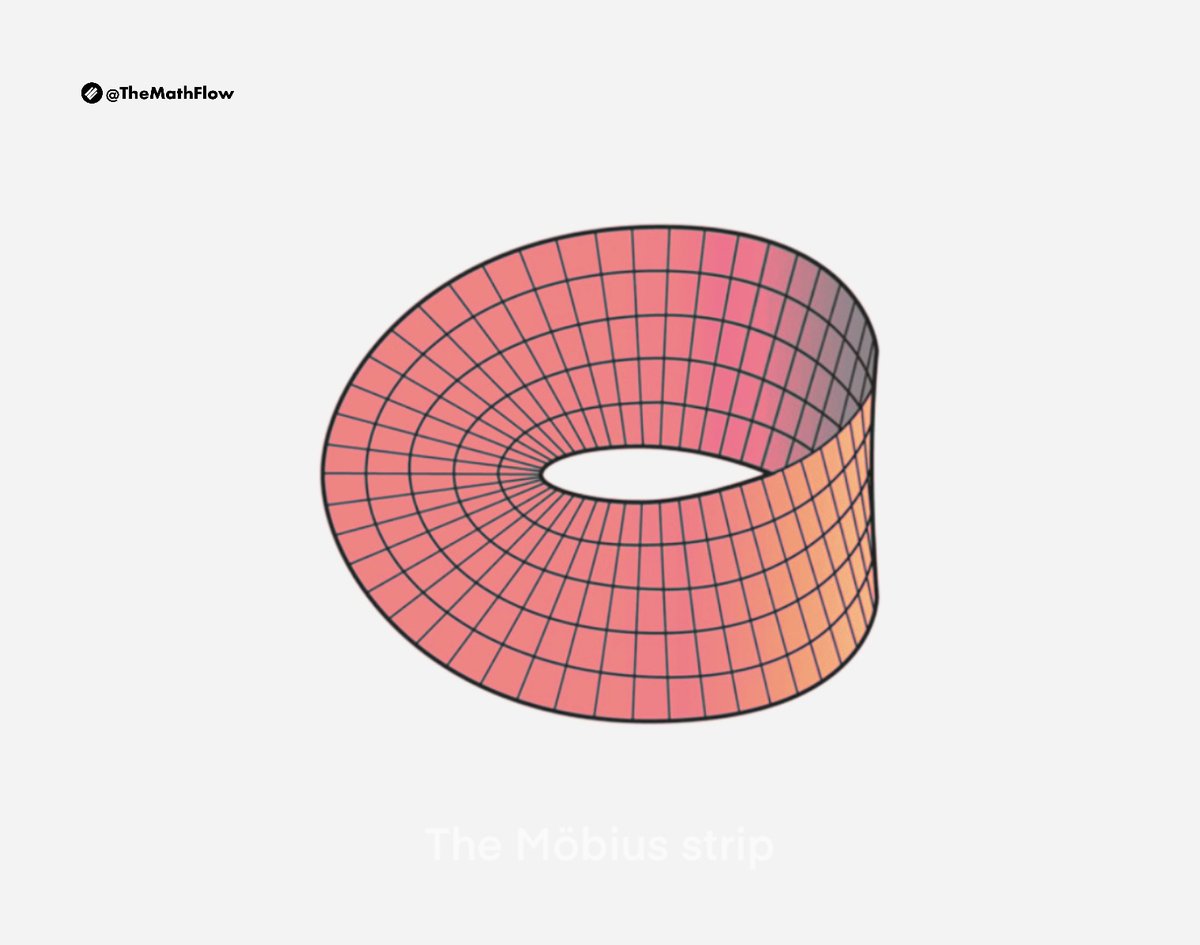
A mathematician named Klein Thought the Möbius band was divine. Said he: “If you glue The edges of two, You’ll get a weird bottle like mine.” - Anonymous
“Obvious” is the most dangerous word in mathematics. - E. T. Bell

There is an infinite number of prime numbers, and as yet-despite millions of man-hours spent in vain, one has not found an efficient closed-form formula to predict them.🤷♂️

The decimal number system used globally today does have its origins in 6th-century India. Indian mathematicians developed the concept of zero and a place-value system. These ideas were later adopted and spread by Arab scholars to Europe, where the system became widely used.

The beauty of mathematics resides in its patterns and symmetries.
These days, we might take nothing for granted, but zero has not always been around. It was the Indians who made it a number in its own right. This breakthrough paved the way for negative numbers, i.e. numbers that are less than zero.








